-
摘要:
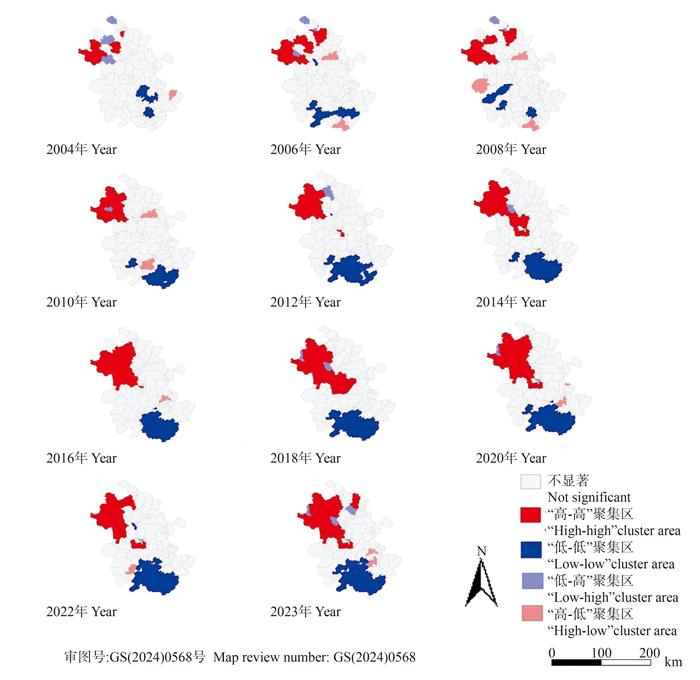
目的 探讨2004―2023年安徽省人类免疫缺陷病毒(human immunodeficiency virus, HIV)/艾滋病(acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, AIDS)患者的时空分布特征,为制定AIDS防治策略提供建议。 方法 基于2004―2023年安徽省104个区(县)历年报告的HIV/AIDS病例数,使用GeoDa 1.22软件进行全局空间自相关和局部空间自相关分析,使用SaTScan 10.2.5软件进行时空扫描分析获得AIDS疫情聚集特点,采用QGIS 3.30软件绘制聚集区和可视化结果,描述分析近20年疫情空间分布。 结果 2004―2023年安徽省AIDS病例空间分布扩大且局部集中,全局莫兰指数(Moran′s I)范围为0.254 9~0.579 1,Z值均>1.96且P < 0.01,2004―2023年存在全局空间自相关。时空扫描结果显示存在3个统计显著聚集区(均P<0.001)。 结论 2004―2023年安徽省AIDS“高-高”聚集区集中于皖北地区,并逐渐扩大至周围地区,提示安徽省西北部为防控重点,应有针对性地实施防控措施。 Abstract:Objective To explore the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of HIV-infected persons and patients in Anhui Province from 2004 to 2023, and to provide suggestions for prevention and treatment strategies. Methods Based on HIV/AIDS cases reported in 104 counties and districts in Anhui Province from 2004 to 2023, global and local spatial autocorrelation analyses were conducted using GeoDa 1.22, while spatio-temporal scanning analyses were performed with SaTScan 10.2.5. The results were visualized using QGIS 3.30 to describe and analyze the spatial distribution of the epidemic over the past 20 years. Results The spatial distribution of AIDS cases in Anhui Province from 2004 to 2023 expanded with local concentrations. Global Moran′s I ranged from 0.254 9 to 0.579 1, with all Z-values >1.96 and P < 0.01, indicating significant global spatial autocorrelation. The spatio-temporal scan identified three statistically significant clusters (all P < 0.001). Conclusions Over the past 20 years, the high and high concentration of AIDS areas in northern Anhui have gradually expanded. This suggests that northwest Anhui is a key focus for prevention and control, requiring targeted measures based on local conditions. -
表 1 2004―2023年安徽省HIV/AIDS病例总体空间自相关分析
Table 1. Global spatial autocorrelation analysis of HIV/AIDS cases in Anhui Province from 2004 to 2023
年份
YearMoran′s I Z值
valueP值
value年份
YearMoran′s I Z值
valueP值
value2004 0.254 9 4.604 8 0.005 2014 0.464 8 7.775 7 0.001 2005 0.366 1 6.377 9 0.001 2015 0.542 7 8.979 1 0.001 2006 0.424 3 7.174 9 0.001 2016 0.538 8 9.084 1 0.001 2007 0.380 0 6.442 8 0.001 2017 0.506 4 8.361 7 0.001 2008 0.435 9 7.415 6 0.001 2018 0.579 1 9.405 5 0.001 2009 0.428 4 7.415 6 0.001 2019 0.524 9 8.717 7 0.001 2010 0.474 3 8.006 8 0.001 2020 0.560 4 9.132 3 0.001 2011 0.395 2 6.689 2 0.001 2021 0.567 5 9.294 3 0.001 2012 0.398 9 6.761 9 0.001 2022 0.553 4 8.931 2 0.001 2013 0.482 2 8.121 7 0.001 2023 0.512 7 8.464 0 0.001 注:HIV,人类免疫缺陷病毒; AIDS,艾滋病。
Note: HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. -
[1] 孙舒曼, 李智明, 张辉国, 等. 2011—2016年中国艾滋病疫情时空特征分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(12): 1207-1210, 1215. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.12.002.Sun SM, Li ZM, Zhang HG, et al. Temporal-spatial characteristic analysis of AIDS/HIV epidemic during 2011-2016 in China[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(12): 1207-1210, 1215. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.12.002. [2] Xu B, Li J, Wang M. Epidemiological and time series analysis on the incidence and death of AIDS and HIV in China[J]. BMC Public Health, 2020, 20(1): 1906. DOI: 10.1186/s12889-020-09977-8. [3] Xie ZY, Chen BW, Duan ZZ. Spatiotemporal analysis of HIV/AIDS incidence in China from 2009 to 2019 and its association with socioeconomic factors: geospatial study[J]. JMIR Public Health Surveill, 2024, 10: e56229. DOI: 10.2196/56229. [4] 杨春利, 戴玉柱, 蔡玉春, 等. 2004—2017年中国大陆AIDS疫情时空分布特征分析[J]. 现代检验医学杂志, 2022, 37(1): 1-6. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7414.2022.01.001.Yang CL, Dai YZ, Cai YC, et al. Temporal-spatial characteristic analysis of AIDS epidemic during 2004~2017 in China's mainland[J]. J Mod Lab Med, 2022, 37(1): 1-6. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7414.2022.01.001. [5] 何佳晋, 袁璐, 吴超. 2010—2019年中国艾滋病流行时空分布特征[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2022, 26(5): 541-546. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2022.05.009.He JJ, Yuan L, Wu C. Temporal-spatial distribution of AIDS epidemic in China, 2010-2019[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2022, 26(5): 541-546. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2022.05.009. [6] 张永树, 杨振凯, 訾璐, 等. 中国艾滋病空间格局和时空演化分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2020, 22(2): 198-206.Zhang YS, Yang ZK, Zi L, et al. Spatio-temporal evolution of the AIDS pattern in China[J]. J Geo Inf Sci, 2020, 22(2): 198-206. [7] 张克春, 付笑冰, 刘珺, 等. 2007—2017年广东省HIV/AIDS流行时空分布特征[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2018, 22(12): 1211-1215. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.12.003.Zhang KC, Fu XB, Liu J, et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics of HIV/AIDS in Guangdong Province, 2007-2017[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2018, 22(12): 1211-1215. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2018.12.003. [8] 张娜, 杨兴光, 王国永, 等. 山东省2009: 2015年HIV/AIDS流行的时空分布特征[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(2): 226-230. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.02.018.Zhang N, Yang XG, Wang GY, et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics of HIV/AIDS in Shandong Province, 2009-2015[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2017, 38(2): 226-230. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.02.018. [9] Han J, Li J, Zang CP, et al. Analysis of inter-provincial movement and the effect of antiretroviral therapy of HIV/AIDS cases after first follow up in China, 2016-2018[J]. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi, 2021, 42(1): 126-130. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20200603-00805. [10] 安徽省统计局, 安徽省第七次全国人口普查领导小组办公室. 2020安徽省人口普查年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020: 26-468.Anhui Provincial Bureau of Statistics, Anhui Provincial Office of the Leading Group for the Seventh National Population Census. 2020 Anhui Provincial population census yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2020: 26-468. [11] Huang G, Cheng W, Xu Y, et al. Spatiotemporal pattern and its determinants for newly reported HIV/AIDS among older adults in Eastern China from 2004 to 2021: retrospective analysis study[J]. JMIR Public Health Surveill, 2024, 10: e51172. DOI: 10.2196/51172. [12] Chu XJ, Song DD, Chu N, et al. Spatial and temporal analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Anhui Province from 2011 to 2023[J]. J Epidemiol Glob Health, 2024, 14(3): 503-512. DOI: 10.1007/s44197-024-00235-3. [13] 计国平, 徐杰, 李晓静, 等. 安徽省男男性行为人群艾滋病知识知晓率及其相关因素分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2011, 15(7): 568-570. https://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201107004Ji GP, Xu J, Li XJ, et al. HIV/AIDS awareness and related factors among MSM in Anhui Province, China[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2011, 15(7): 568-570. https://zhjbkz.ahmu.edu.cn/article/id/JBKZ201107004 [14] 肖永康, 徐增辉, 刘爱文, 等. 皖北地区中老年女性HIV/AIDS患者身体与心理健康状况调查[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2021, 25(12): 1398-1402. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2021.12.007.Xiao YK, Xu ZH, Liu AW, et al. Survey of physical and mental health among middle-old aged female HIV/AIDS patients in North Anhui Province[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2021, 25(12): 1398-1402. DOI: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2021.12.007. [15] Li L, Sun GQ, Zhong P, et al. HIV-1 Thai B strain has spread out of former plasma donors into general population through sexual contact in Henan, China[J]. J Med Virol, 2016, 88(4): 614-621. DOI: 10.1002/jmv.24383. [16] Mao NL, Pan HF, Lu MM, et al. AIDS awareness and condom use among patients in a high-HIV-prevalence area in rural northern Anhui, China[J]. J Investig Med, 2010, 58(6): 801-803. DOI: 10.231/JIM.0b013e3181e80188. -





 下载:
下载: