Construction and validation of a prediction model for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease based on machine learning
-
摘要:
目的 构建及验证用于预测非酒精性脂肪性肝病(non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, NAFLD)的机器学习(machine learning, ML)模型,并筛选出最优模型,通过SHapley加性解释(SHapley Additive exPlanations, SHAP)框架解释该模型。 方法 选取美国国家健康与营养调查数据库中2017年1月―2020年3月的数据,按7∶3随机分为训练集和测试集。最小绝对收缩和选择算子回归用于特征选择,采用6种算法构建预测模型。使用受试者工作特征曲线下面积(area under curve, AUC)对模型进行评价,并通过校准曲线、决策曲线分析、变量重要性图、SHAP图进行解释。 结果 6 918名研究对象中,3 974人(57.44%)被诊断为NAFLD。极限梯度提升(eXtreme gradient boosting, XGBoost)模型综合表现优于其他模型,在测试集上的AUC为0.851,准确率为0.757,灵敏度为0.760,特异度为0.754。主要预测因子包括身体圆度指数、腰围、三酰甘油-葡萄糖指数、谷丙转氨酶、糖化血红蛋白和高密度脂蛋白胆固醇。在模型应用方面,开发了一个用户界面供医务人员使用。 结论 研究构建并验证了6种用于预测NAFLD的ML模型,其中XGBoost模型更具优势,可为临床早期筛查NAFLD高危患者提供可靠的参考依据。 Abstract:Objective This study aimed to construct and validate machine learning (ML) models for predicting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), screen out the optimal model, and interpret it through the SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) framework. Methods The data in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surve database from January 2017 to March 2020 were randomly divided into a training set and a test set at a ratio of 7∶3. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression was employed for feature selection, and six algorithms were used to construct the prediction models. The models were evaluated using the area under curve (AUC) and interpreted by the calibration curves, the decision curve analysis, variable importance plot, and SHAP plot. Results Of the 6 918 participants, 3 974 (57.44%) were diagnosed with NAFLD. The overall performance of eXtreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) model was better than other models, with an AUC of 0.851, an accuracy of 0.757, a sensitivity of 0.760 and a specificity of 0.754 on the test set. The main predictors were body roundness index, waist circumference, triglyceride glucose index, alanine aminotransferase, glycated hemoglobin and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. In terms of model application, a user interface was developed for use by medical staff. Conclusions In this study, six ML models for predicting NAFLD were constructed and validated, among which XGBoost was more advantageous and could provide a reliable reference for early clinical screening of high-risk patients with NAFLD. -
Key words:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease /
- Machine learning /
- Prediction model
-
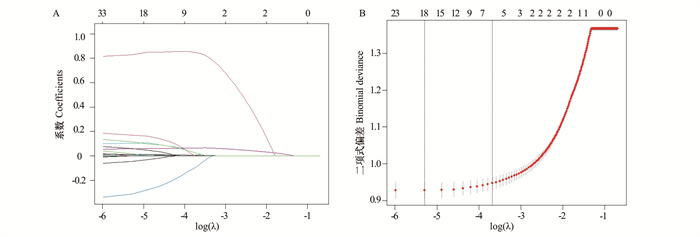
图 2 模型评价
A:不同模型在测试集上的受试者工作特征曲线;B:不同模型在测试集上的决策曲线分析;C:不同模型在测试集上的校准曲线;AUC:受试者工作特征曲线下面积;DT:决策树;EN:弹性网络;LR:逻辑回归;MLP:多层感知器;SVM:支持向量机;XGBoost:极限梯度提升。
Figure 2. Model evaluation
A: the receiver operating characteristic curves of different models on the test set; B: decision curve analysis of different models on the test set; C: calibration curves of different models on the test set; AUC: area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; DT: decision tree; EN: elastic net; LR: logistic regression; MLP: multilayer perceptron; SVM: support vector machine; XGBoost: eXtreme gradient boosting.
图 3 使用SHAP直观地解释机器学习模型
A:根据平均(|SHAP值|)对不同变量进行重要性排序;B:SHAP摘要图;SHAP:SHapley加性解释;WC:腰围;BRI:身体圆度指数;TyG:三酰甘油-葡萄糖指数;HbA1c:糖化血红蛋白;HDL-C,高密度脂蛋白胆固醇。
Figure 3. Visually interpret machine learning model by using SHAP
A: the importance of different variables was ranked according to the average (|SHAP value |); B: SHAP summary plot; SHAP: SHapley Additive exPlanations; WC: waist circumference; BRI: body roundness index; TyG: triglyceride-glucose index; HbA1c: glycosylated hemoglobin; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
表 1 非NAFLD组和NAFLD组的基线特征比较
Table 1. Comparison of baseline characteristics in the non-NAFLD and NAFLD groups
变量Variable 非NAFLD组Non NAFLD group① (n=2 944) NAFLD组NAFLD group① (n=3 974) Z/χ2值value P值value 年龄/岁Age/years 43.00(27.00, 62.00) 54.00(39.00, 65.00) -15.22 < 0.001 性别Gender 31.55 < 0.001 男性Male 1 314(44.63) 2 045(51.46) 女性Female 1 630(55.37) 1 929(48.54) 种族Race 96.25 < 0.001 非西班牙裔白人Non-Hispanic whites 921(31.28) 1 337(33.64) 非西班牙裔黑人Non-Hispanic blacks 897(30.47) 908(22.85) 非西班牙裔亚裔Non-Hispanic Asian 410(13.93) 490(12.33) 墨西哥裔美国人Mexican Americans 265(9.00) 600(15.10) 其他西班牙裔Other Hispanics 301(10.22) 449(11.30) 其他种族Other races 150(5.10) 190(4.78) BMI/(kg·m-2) 25.10(22.10, 28.60) 31.60(27.70, 36.70) -42.25 < 0.001 臂围Arm circumference/cm 30.60(27.80, 33.70) 35.20(32.10, 38.70) -37.05 < 0.001 腰围Waist circumference/cm 88.50(79.88, 97.80) 106.60(97.33, 118.20) -46.28 < 0.001 血尿素氮Blood urea nitrogen/(mmol·L-1) 5.00(3.93, 6.07) 5.00(4.28, 6.07) -5.48 < 0.001 血清肌酐Serum creatinine/(μmol·L-1) 74.26(62.76, 87.52) 75.14(62.76, 88.40) -0.83 0.407 血清尿酸Serum uric acid/(μmol·L-1) 291.50(243.90, 340.84) 333.10(279.60, 386.60) -20.87 < 0.001 白蛋白Albumin/(g·L-1) 41.00(39.00, 43.00) 41.00(38.00, 43.00) -9.72 < 0.001 碱性磷酸酶Alkaline phosphatase/(U·L-1) 72.00(59.00, 85.00) 77.43(66.00, 92.00) -12.69 < 0.001 球蛋白Globulin/(g·L-1) 30.00(28.00, 33.00) 31.00(28.35, 34.00) -6.92 < 0.001 ALT/(U·L-1) 15.00(11.35, 20.00) 20.00(14.00, 28.00) -23.78 < 0.001 AST/(U·L-1) 18.00(15.84, 22.00) 19.00(16.00, 24.00) -7.72 < 0.001 GGT/(U·L-1) 17.00(12.00, 23.79) 24.00(17.00, 34.00) -25.51 < 0.001 总胆红素Total bilirubin/(μmol·L-1) 6.84(5.13, 10.26) 6.84(5.13, 8.55) -3.22 0.001 总蛋白Total protein/(g·L-1) 72.00(69.00, 74.00) 72.00(69.00, 74.00) -0.75 0.456 乳酸脱氢酶Lactate dehydrogenase/(U·L-1) 151.00(135.00, 170.00) 156.00(141.00, 174.00) -7.92 < 0.001 TC/(mmol·L-1) 4.58(4.01, 5.22) 4.78(4.14, 5.41) -7.29 < 0.001 TG/(mmol·L-1) 1.01(0.76, 1.40) 1.52(1.10, 2.11) -31.48 < 0.001 FPG/(mmol·L-1) 5.00(4.66, 5.33) 5.33(4.94, 6.00) -25.79 < 0.001 HDL-C/(mmol·L-1) 1.43(1.22, 1.68) 1.19(1.03, 1.42) 27.16 < 0.001 白细胞White blood cell/(×109·L-1) 6.50(5.40, 7.80) 7.20(6.02, 8.60) -15.36 < 0.001 中性粒细胞Neutrophils/(×109·L-1) 3.62(2.80, 4.70) 4.10(3.27, 5.20) -12.76 < 0.001 淋巴细胞Lymphocyte/(×109·L-1) 2.00(1.60, 2.40) 2.20(1.80, 2.70) -11.66 < 0.001 红细胞Red blood cell/(×1012·L-1) 4.64(4.34, 4.97) 4.79(4.48, 5.12) -11.99 < 0.001 平均红细胞体积Mean corpuscular volume/fL 89.10(86.00, 92.03) 88.20(85.00, 91.20) -7.05 < 0.001 血小板Platelet/(×109·L-1) 237.00(203.00, 276.00) 244.00(207.25, 286.00) -5.00 < 0.001 糖化血红蛋白Glycosylated hemoglobin/% 5.40(5.20, 5.70) 5.70(5.40, 6.30) -25.79 < 0.001 SBP/mmHg 116.79(107.67, 130.67) 123.67(113.33, 135.33) -13.39 < 0.001 DBP/mmHg 70.33(64.67, 77.08) 75.33(69.00, 82.00) -18.60 < 0.001 三酰甘油-葡萄糖指数Triglyceride-glucose index 8.30(7.99, 8.67) 8.81(8.45, 9.22) -35.06 < 0.001 身体圆度指数Body roundness index 4.03(2.97, 5.28) 6.40(5.10, 8.11) -44.58 < 0.001 注:NAFLD,非酒精性脂肪性肝病;ALT,丙氨酸氨基转移酶;AST,天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶;GGT,γ-谷氨酰转移酶;TC,总胆固醇;TG,三酰甘油;FPG,空腹血糖;HDL-C,高密度脂蛋白胆固醇;SBP,收缩压;DBP,舒张压。
①以M(P25, P75)或人数(占比/%)表示。
Note: NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; GGT, gamma glutamyltransferase; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglycerides; FPG, fasting blood glucose; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure.
① M(P25, P75) or number of people (proportion /%).表 2 测试集上机器学习模型的性能
Table 2. Performance of machine learning models on the test set
模型Model AUC 准确率Accuracy 灵敏度Sensitivity 特异度Specificity F1分数F1 score Brier评分Brier score DT 0.825 0.759 0.697 0.804 0.707 0.170 EN 0.838 0.763 0.682 0.821 0.705 0.194 LR 0.843 0.770 0.694 0.824 0.716 0.157 MLP 0.847 0.764 0.723 0.794 0.719 0.179 SVM 0.849 0.771 0.688 0.831 0.714 0.154 XGBoost 0.851 0.757 0.760 0.754 0.722 0.153 注:XGBoost, 极限梯度提升; DT,决策树;EN,弹性网络;LR,逻辑回归;MLP,多层感知器;SVM,支持向量机;XGBoost,极限梯度提升;AUC,曲线下面积。
Note: XGBoost, eXtreme gradient boosting; DT, decision tree; EN, elastic net; LR, logistic regression; MLP, multilayer perceptron; SVM, support vector machine; XGBoost, eXtreme gradient boosting; AUC, area under curve. -
[1] Ji WD, Xue MY, Zhang YS, et al. A machine learning based framework to identify and classify non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a large-scale population [J]. Front Public Health, 2022, 10: 846118. DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.846118. [2] Perakakis N, Polyzos SA, Yazdani A, et al. Non-invasive diagnosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrosis with the use of omics and supervised learning: a proof of concept study [J]. Metabolism, 2019, 101: 154005. DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.154005. [3] Ma XF, Yang C, Liang K, et al. A predictive model for the diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease based on an integrated machine learning method [J]. Am J Transl Res, 2021, 13(11): 12704-12713. [4] Peduzzi P, Concato J, Kemper E, et al. A simulation study of the number of events per variable in logistic regression analysis [J]. J Clin Epidemiol, 1996, 49(12): 1373-1379. DOI: 10.1016/s0895-4356(96)00236-3. [5] Zhao YP, Li HL. Association of serum vitamin C with liver fibrosis in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2022, 57(7): 872-877. DOI: 10.1080/00365521.2022.2041085. [6] Zou HX, Zhao FR, Lyu XH, et al. Development and validation of a new nomogram to screen for MAFLD [J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2022, 21(1): 133. DOI: 10.1186/s12944-022-01748-1. [7] Yuan KC, Tsai LW, Lee KH, et al. The development an artificial intelligence algorithm for early sepsis diagnosis in the intensive care unit [J]. Int J Med Inform, 2020, 141: 104176. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2020.104176. [8] Yi FL, Yang H, Chen DR, et al. XGBoost-SHAP-based interpretable diagnostic framework for Alzheimer′s disease [J]. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak, 2023, 23(1): 137. DOI: 10.1186/s12911-023-02238-9. [9] Dong BT, Zhang H, Duan YY, et al. Development of a machine learning-based model to predict prognosis of alpha-fetoprotein-positive hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. J Transl Med, 2024, 22(1): 455. DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05203-w. [10] Zuo D, Yang LX, Jin Y, et al. Machine learning-based models for the prediction of breast cancer recurrence risk [J]. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak, 2023, 23(1): 276. DOI: 10.1186/s12911-023-02377-z. [11] Ferraioli G, Soares Monteiro LB. Ultrasound-based techniques for the diagnosis of liver steatosis [J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(40): 6053-6062. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i40.6053. -





 下载:
下载: