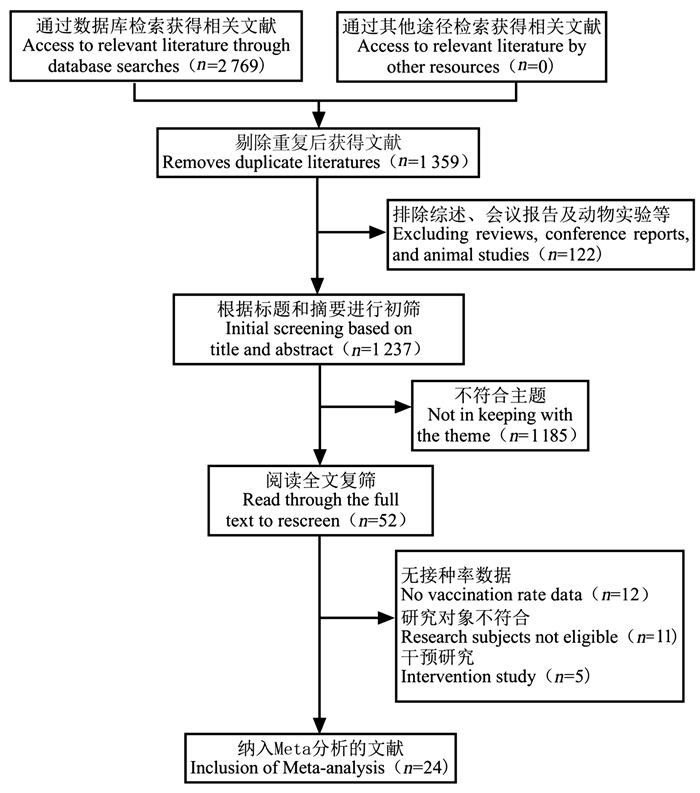
Human papillomavirus vaccination rate and influencing factors among female university students in China: a Meta-analysis
-
摘要:
目的 了解中国女大学生人乳头瘤病毒(human papillomavirus, HPV)疫苗接种率及影响因素。 方法 检索2016年以后女大学生HPV疫苗接种相关文献。使用Stata 17.0软件进行Meta分析。 结果 共纳入24项研究,总样本量为40 320人。Meta分析显示,中国女大学生HPV疫苗接种率为7.56%(95% CI:5.27%~10.21%)。影响因素包括城市户籍(OR=2.50, 95% CI:1.79~3.49)、母亲大专及以上学历(OR=1.59, 95% CI:1.13~2.24)、父亲大专及以上学历(OR=1.56, 95% CI:1.16~2.11)、性行为(OR=1.63, 95% CI:1.38~1.92)、知晓HPV疫苗(OR=4.72, 95% CI:3.26~6.28)及对HPV疫苗认知良好(OR=3.96, 95% CI:1.77~8.87)。 结论 中国女大学生HPV疫苗接种率较低,对HPV疫苗的认知是疫苗接种的重要因素。应加强宣传和教育,提高女大学生对HPV疫苗的认知,以推进HPV疫苗的普及和应用。 Abstract:Objective This study aimed to investigate the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination rate and its influencing factors among female university students in China. Methods We used Stata 17.0 software to conduct a Meta-analysis of articles published since 2016 on HPV vaccination among female university students. Results Twenty-four studies with a total sample size of 40 320 individuals were included. The HPV vaccination rate was 7.56% (95% CI: 5.27%-10.21%). The influencing factors included household registration in an urban area (OR=2.50, 95% CI: 1.79-3.49), mother with a college degree or above (OR=1.59, 95% CI: 1.13-2.24), father with a college degree or above (OR=1.56, 95% CI: 1.16-2.11), sexual behavior (OR=1.63, 95% CI: 1.38-1.92), HPV vaccine awareness (OR=4.72, 95% CI: 3.26-6.28), and good knowledge of HPV vaccine (OR=3.96, 95% CI: 1.77-8.87). Conclusions The HPV vaccination rate is low among female university students in China. Knowledge of HPV vaccine is an important factor influencing vaccination. Publicity and education should be strengthened to raise awareness of the HPV vaccine among female college students, promoting its widespread application. -
Key words:
- Human papillomavirus vaccine /
- Vaccination /
- Female college students
-
表 1 纳入研究基本特征
Table 1. Characteristics of included studies
纳入研究
Included study地区
Region调查年份
Survey year抽样方法
Sampling method样本量
Sample size接种率
Vaccination rate/%影响因素
Influencing factor质量评分/分
Quality score/score张肖肖等(2021)[10]
Zhang XX, et al(2021)[10]全国范围
Nationwide2019 多阶段随机
Multi-stage random3 007 2.96 ③⑦ 6 贾鑫华等(2019)[11]
Jia XH, et al(2019)[11]江西
Jiangxi2018 单纯随机
Simple random2 091 3.30 ― 6 石晶等(2023)[12]
Shi J, et al(2023)[12]北京
Beijing2019 整群抽样
Cluster sampling825 2.91 ― 4 何小桃等(2022)[13]
He XT, et al(2022)[13]广西
Guangxi2022 便利抽样
Convenience sampling628 4.14 ― 5 赖江宜等(2019)[6]
Lai JY, et al(2019)[6]浙江
Zhejiang2019 分层抽样
Stratified sampling220 3.60 ③ 5 冯澜等(2021)[14]
Feng L, et al(2021)[14]广西
Guangxi2020 便利抽样
Convenience sampling337 21.66 ― 8 胡淑怡等(2022)[7]
Hu SY, et al(2022)[7]上海
Shanghai2020 整群抽样
Cluster sampling1 992 8.38 ①②③④⑤⑧ 6 李君等(2021)[15]
Li J, et al(2021)[15]全国范围
Nationwide2019 分层抽样
Stratified sampling2 295 10.35 ①② 8 范伟超等(2022)[16]
Fan WC, et al(2022)[16]广东
Guangdong2020 便利抽样
Convenience sampling587 14.82 ― 8 邓景景等(2021)[17]
Deng JJ, et al(2021)[17]江苏
Jiangsu2019 分层抽样
Stratified sampling2 169 7.98 ⑥ 5 刘敏等(2021)[18]
Liu M, et al(2021)[18]山东
Shangdong2020 分层抽样
Stratified sampling408 21.32 ― 8 陈慧等(2021)[19]
Chen H, et al(2021)[19]四川
Sichuan2020 便利抽样
Convenience sampling462 3.46 ― 6 肖玲等(2022)[20]
Xiao L, et al(2022)[20]湖北
Hubei2021 分层抽样
Stratified sampling6 459 13.30 ― 8 陈虹君等(2023)[21]
Chen HJ, et al(2023)[21]新疆
Xinjiang2022 便利抽样
Convenience sampling1 164 11.77 ②③④⑤⑥⑦ 4 郑浩等(2021)[22]
Zheng H, et al (2021)[22]浙江
Zhejiang2021 分层抽样
Stratified sampling1 092 3.29 ― 5 张希等(2021)[23]
Zhang X, et al(2021)[23]山西、四川
Shanxi, Sichuan2020 便利抽样
Convenience sampling975 2.15 ― 7 Liu YN, et al(2020)[3] 北京
Beijing2018 单纯随机
Simple random453 9.49 ― 8 You DY, et al(2020)[2] 全国范围
Nationwide2019 便利抽样
Convenience sampling4 220 10.97 ①②③④⑤⑧ 5 Deng C, et al(2021)[24] 全国范围
Nationwide2019 便利抽样
Convenience sampling755 3.58 ― 7 Liu YN, et al(2021)[8] 北京
Beijing2018 便利抽样
Convenience sampling589 8.66 ③⑥⑧ 7 Ma Y, et al(2021)[1] 广东
Guangdong2018 分层抽样
Stratified sampling3 832 3.50 ①⑥⑦⑧ 6 Si MY, et al(2021)[25] 全国范围
Nationwide2020 便利抽样
Convenience sampling3 867 2.64 ― 7 Huang Y, et al(2022)[26] 全国范围
Nationwide2022 分层抽样
Stratified sampling1 438 34.21 ― 7 Wang H, et al(2022)[27] 河南
Henan2020 便利抽样
Convenience sampling455 1.32 ― 7 注:①户籍地; ②民族; ③专业; ④父亲学历; ⑤母亲学历; ⑥性行为; ⑦知晓HPV疫苗; ⑧HPV疫苗认知良好; “―”,无法获取。
Note:① Household registration; ② Nationality; ③ Major; ④ Father′s education; ⑤ Mother′s education; ⑥ Sexual behavior; ⑦ Awareness of HPV vaccine; ⑧ Good knowledge of HPV vaccine; "―",unavailable.表 2 HPV疫苗接种率的亚组分析和Meta回归分析
Table 2. Subgroup and Meta-regression analyses of HPV vaccination rate
亚组
Subgroup研究数量
Number of study接种率
Vaccination rate/%
(95% CI)异质性Heterogeneity β值
valueP值
valueI2/% P值value 地区Region 东部Eastern 10 7.61(5.07~10.62) 96.75 <0.001 ① 中西部Central and western 8 6.40(2.90~11.13) 98.61 <0.001 -0.688 0.091 全国范围Nationwide 6 9.07(3.33~17.24) 99.57 <0.001 -0.306 0.539 调查年份Survey year 2018 4 5.73(3.42~8.58) 94.14 <0.001 ① 2019 7 5.84(3.24~9.14) 98.00 <0.001 0.081 0.871 2020 8 7.76(3.81~12.95) 98.28 <0.001 0.148 0.748 2021 2 11.48(10.77~12.21) 99.53 <0.001 -0.234 0.713 2022 3 14.73(2.30~35.17) 99.52 <0.001 1.519 0.008 年龄组/岁Age group/ years ≤22 4 4.61(1.43~9.42) 97.03 <0.001 ― ― >22 2 18.25(15.68~20.97) 79.09 <0.001 ― ― 年级Grade 大一~大二First and second year 8 4.38(2.33~7.03) 97.26 <0.001 ― ― 大三及以上Third year and above 4 10.45(4.54~18.38) 97.84 <0.001 ― ― 抽样方法Sampling method 随机Random 13 8.35(4.96~12.52) 99.16 <0.001 -0.231 0.584 非随机Nonrandom 11 6.66(3.85~10.16) 98.05 <0.001 ① 样本量Sample size ≤1 000 12 6.85(3.83~10.64) 96.76 <0.001 ① >1 000 12 8.27(5.01~12.26) 99.32 <0.001 0.542 0.188 质量评分/分Quality score/score ≤7 18 5.60(3.40~8.32) 98.81 <0.001 ① >7 6 7.56(5.27~10.21) 98.85 <0.001 1.612 < 0.001 注:HPV,人乳头瘤病毒; I2, 异质性指数。
①作为参考水平; “―”,数据无法获取,因为提供年龄及年级具体信息的研究较少,数据缺失较多,所以无法纳入多因素的Meta回归分析,只能进行亚组分析。
Note: HPV, human papillomavirus; I2, I-squared statistic.
① Reference level; "―",data cannot be obtained, due to the lack of research providing specific information on age and grade level, there are many missing data, so it is not possible to include multiple factor Meta regression analysis, and only subgroup analysis can be conducted.表 3 HPV疫苗接种影响因素分析
Table 3. Analysis of factors influencing HPV vaccination
影响因素Influencing factor 研究数量
Number of study异质性
HeterogeneityOR值value
(95% CI)P值
valueI2/% P值value 城市Urban 4 75.52 0.007 2.50(1.79~3.49) <0.001 汉族Han ethnic 4 83.76 <0.001 1.10(0.65~1.86) 0.719 医学专业Medical 6 20.67 0.278 1.13(0.97~1.31) 0.118 父亲学历(大专及以上) Father′s education level (college or above) 3 63.27 0.066 1.56(1.16~2.11) 0.004 母亲学历(大专及以上) Mother′s education level (college or above) 3 69.03 0.040 1.59(1.13~2.24) 0.008 性行为Sexual behavior 4 44.97 0.142 1.63(1.38~1.92) <0.001 知晓HPV疫苗Awareness of HPV vaccine 3 64.85 0.058 4.72(3.26~6.82) <0.001 HPV疫苗认知良好Good knowledge of HPV vaccine 4 92.74 <0.001 3.96(1.77~8.87) 0.001 注:HPV,人乳头瘤病毒; I2, 异质性指数。
Note:HPV, human papillomavirus; I2, I-squared statistic. -
[1] Ma Y, Wang CX, Liu FH, et al. Human papillomavirus vaccination coverage and knowledge, perceptions and influencing factors among university students in Guangzhou, China[J]. Hum Vaccines Immunother, 2021, 17(10): 3603-3612. DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2021.1927411. [2] You DY, Han LY, Li L, et al. Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine uptake and the willingness to receive the HPV vaccination among female college students in China: a multicenter study[J]. Vaccines, 2020, 8(1): 31. DOI: 10.3390/vaccines8010031. [3] Liu YN, Di N, Tao X. Knowledge, practice and attitude towards HPV vaccination among college students in Beijing, China[J]. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2020, 16(1): 116-123. DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1638727. [4] Chen JL, Zhang ZN, Pan WY, et al. Estimated human papillomavirus vaccine coverage among females 9-45 years of age - China, 2017-2022[J]. China CDC Wkly, 2024, 6(19): 413-417. DOI: 10.46234/ccdcw2024.080. [5] 卫飞雪, 崔雪莲, 郭蒙, 等. 广西柳州地区大学生人乳头瘤病毒感染自然史的前瞻性研究[J]. 病毒学报, 2018, 34(4): 515-521.Wei FX, Cui XL, Guo M, et al. Natural history of human papillomavirus infection among college students in Liuzhou, Guangxi of China: a prospective study[J]. Chin J Virol, 2018, 34(4): 515-521. [6] 赖江宜, 吴夏秋. 杭州市女大学生人乳头瘤病毒及其疫苗认知和接种意愿调查[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2019, 25(3): 303-307. DOI: 10.19914/j.cjvi.2019.03.016.Lai JY, Wu XQ. Knowledge about human papillomavirus (HPV) and HPV vaccine and willingness to receive HPV vaccination among female college students of Hangzhou city[J]. Chinese Journal of Vaccines and Immunization, 2019, 25(3): 303-307. DOI: 10.19914/j.cjvi.2019.03.016. [7] 胡淑怡, 胡晓宇, 许洁霜, 等. 女大学生对HPV及其疫苗认知情况调查研究[J]. 中国妇幼健康研究, 2022, 33(4): 75-81. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5293.2022.04.014.Hu SY, Hu XY, Xu JS, et al. A survey on the cognition of HPV and its vaccine among female college students[J]. Chinese Journal of Woman and Child Health Research, 2022, 33(4): 75-81. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5293.2022.04.014. [8] Liu YN, Jiang XY, Xu LY, et al. Difference between medical and nonmedical students on knowledge, practice, and attitude towards the human papillomavirus vaccine in China: a cross-sectional study[J]. J Cancer Educ, 2021, 36(5): 1014-1021. DOI: 10.1007/s13187-019-01682-4. [9] 张肖肖, 史金晶, 张延炀, 等. 中国大陆高校大学生人乳头瘤病毒疫苗知晓度和接种意愿Meta分析[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2019, 25(3): 308-312. DOI: 10.19914/j.cjvi.2019.03.017.Zhang XX, Shi JJ, Zhang YY, et al. Awareness of human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine and willingness to receive HPV vaccination among college students in Chinese mainland: a Meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Vaccines and Immunization, 2019, 25(3): 308-312. DOI: 10.19914/j.cjvi.2019.03.017. [10] 张肖肖, 史金晶, 张旋, 等. 2019年大学女生人乳头瘤病毒疫苗知晓率和接种率调查[J]. 中国疫苗和免疫, 2021, 27(4): 458-461, 467. DOI: 10.19914/j.CJVI.2021079.Zhang XX, Shi JJ, Zhang X, et al. Awareness and coverage of human papillomavirus vaccine among female university students in 2019[J]. Chinese Journal of Vaccines and Immunization, 2021, 27(4): 458-461, 467. DOI: 10.19914/j.CJVI.2021079. [11] 贾鑫华, 许琪, 杨红, 等. 赣州市女大学生对HPV及其疫苗的认知情况与接种意愿调查分析[J]. 实用临床医学, 2019, 20(3): 86-90, 102. DOI: 10.13764/j.cnki.lcsy.2019.03.030.Jia XH, Xu Q, Yang H, et al. An investigation on HPV cognition status and vaccination intention of female college students in Ganzhou[J]. Pract Clin Med, 2019, 20(3): 86-90, 102. DOI: 10.13764/j.cnki.lcsy.2019.03.030. [12] 石晶, 赵春艳, 孙远洁, 等. 北京市某区大学生HPV及其疫苗认知和接种意愿调查[J]. 中国校医, 2023, 37(2): 81-85. DOI: 10.20161/j.cnki.32-1199/r.2023.02.002.Shi J, Zhao CY, Sun YJ, et al. Investigation on HPV and its vaccine cognition and vaccination willingness of college students in a district of Beijing[J]. Chin J School Doctor, 2023, 37(2): 81-85. DOI: 10.20161/j.cnki.32-1199/r.2023.02.002. [13] 何小桃, 覃芳, 邓金铃, 等. 广西两所高校大学生对HPV及其疫苗认知和疫苗接种意愿调查[J]. 应用预防医学, 2022, 28(2): 153-156.He XT, Xun F, Deng JL, et al. A survey on the knowledge of HPV and its vaccine and the willingness to vaccinate among college students in two universities in Guangxi[J]. Applied Prev Med, 2022, 28(2): 153-156. [14] 冯澜, 吴腾燕. 南宁市部分高校女大学生对HPV疫苗认知及接种意愿调查[J]. 中国初级卫生保健, 2021, 35(1): 65-68.Feng L, Wu TY, et al. Survey on the knowledge of HPV vaccine and willingness to be vaccinated among female college students in some universities in Nanning[J]. Chinese Primary Health Care, 2020, 35(1): 65-68. [15] 李君, 石雅佳, 王洪岩, 等. 倾向性评分匹配分析大学生HPV疫苗接种的影响因素[J]. 现代预防医学, 2021, 48(15): 2819-2824. DOI: 10.20043/j.cnki.mpm.2021.15.028.Li J, Shi YJ, Wang HY, et al. Propensity score matching analysis of influencing factors of HPV vaccination in college students[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2021, 48(15): 2819-2824. DOI: 10.20043/j.cnki.mpm.2021.15.028. [16] 范伟超, 杨钊泳, 陈奕帆, 等. 深圳市大学生对HPV及其疫苗认知、接种意愿调查[J]. 职业与健康, 2022, 38(11): 1554-1559. DOI: 10.13329/j.cnki.zyyjk.2022.0324.Fan WC, Yang ZY, Chen YF, et al. Investigation on cognition and willingness of college students to HPV and its vaccine in Shenzhen City[J]. Occup and Health, 2022, 38(11): 1554-1559. DOI: 10.13329/j.cnki.zyyjk.2022.0324. [17] 邓景景, 张钧, 刘娜, 等. 苏州市大学女生子宫颈癌防控认知调查[J]. 公共卫生与预防医学, 2021, 32(4): 116-119. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2483.2021.04.027.Deng JJ, Zhang J, Liu N, et al. Investigation on the cognition of prevention and control of cervical cancer among female college students in Suzhou[J]. J Pub Health Prev Med, 2021, 32(4): 116-119. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2483.2021.04.027. [18] 刘敏, 尹文强, 许小凤, 等. 潍坊市女大学生人乳头瘤病毒疫苗接种犹豫现状及影响因素[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2021, 42(2): 257-259, 263. DOI: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2021.02.024.Liu M, Yin WQ, Xu XF, et al. Study on HPV vaccine hesitation and associated factors among female college students in Weifang[J]. Chin J Sch Health, 2021, 42(2): 257-259, 263. DOI: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2021.02.024. [19] 陈慧, 周静, 黄倩, 等. 西部地区大学生人乳头瘤病毒疫苗的接种现状及其对人乳头瘤病毒和疫苗的认知、态度及影响因素[J]. 中国医学科学院学报, 2021, 43(4): 545-550. DOI: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.13153.Chen H, Zhou J, Huang Q, et al. Status of human papillomavirus vaccination and knowledge, attitudes, and influencing factors towards human papillomavirus and its vaccines among university students in western China[J]. Acta Acad Med Sin, 2021, 43(4): 545-550. DOI: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.13153. [20] 肖玲, 黄光梅, 张雪丽, 等. 襄阳市大学生对宫颈癌防控的认知及HPV疫苗接种意愿调查分析[J]. 公共卫生与预防医学, 2022, 33(3): 104-108. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2483.2022.03.024.Xiao L, Huang GM, Zhang XL, et al. Cognition of prevention and control of cervical cancer and influencing factors of HPV vaccination intention among college students in Xiangyang[J]. J Pub Health Prev Med, 2022, 33(3): 104-108. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2483.2022.03.02. [21] 陈虹君, 王维, 谢香芹, 等. 医学院校女大学生对HPV及疫苗的认知与接种意愿调研: 以新疆第二医学院为例[J]. 黑龙江科学, 2023, 14(1): 50-55. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8646.2023.01.013.Chen HJ, Wang W, Xie XQ, et al. Investigation on female medical college students' cognition and vaccination willingness to HPV and vaccine: through taking Xinjiang second medical college as an example[J]. Heilongjiang Science, 2023, 14(1): 50-55. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8646.2023.01.013. [22] 郑浩, 沈芳宁, 张也妮, 等. 浙江省女大学生HPV疫苗认知度与接种意愿[J]. 湖州师范学院学报, 2021, 43(10): 74-80.Zheng H, Shen FN, Zhang YN, et al. Awareness and willingness of HPV vaccination among female college students in Zhejiang Province[J]. Journal of Huzhou University, 2021, 43(10): 74-80. [23] 张希, 陈慧, 孙莉颖, 等. 中西部地区女大学生HPV疫苗接种意愿的影响因素研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2021, 48(23): 4265-4271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8507.2021.23.xdyfyx202123010Zhang X, Chen H, Sun LY, et al. Influencing factors on HPV vaccination willingness among college female students in central and western China[J]. Mod Prev Med, 2021, 48(23): 4265-4271. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8507.2021.23.xdyfyx202123010 [24] Deng C, Chen XL, Liu YQ. Human papillomavirus vaccination: coverage rate, knowledge, acceptance, and associated factors in college students in mainland China[J]. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2021, 17(3): 828-835. DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1797368. [25] Si MY, Jiang Y, Su XY, et al. Willingness to accept human papillomavirus vaccination and its influencing factors using information-motivation-behavior skills model: a cross-sectional study of female college freshmen in mainland China[J]. Cancer Control, 2021, 28: 10732748211032899. DOI: 10.1177/10732748211032899. [26] Huang Y, Chen C, Wang L, et al. HPV vaccine hesitancy and influencing factors among university students in China: a cross-sectional survey based on the 3Cs model[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19(21): 14025. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192114025. [27] Wang H, Wang XY, Chen PP, et al. Factors influencing Chinese female college students' willingness to receive human papillomavirus vaccine: a cross-sectional study based on information-motivation-behavioral skills model[J]. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2022, 18(7): 2140550. DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2140550. [28] Natipagon-Shah B, Lee E, Lee SY. Knowledge, beliefs, and practices among U. S. college students concerning papillomavirus vaccination[J]. J Community Health, 2021, 46(2): 380-388. DOI: 10.1007/s10900-020-00922-9. -





 下载:
下载: