Effect of community public health comprehensive intervention on blood pressure control among people at different risk of cardiovascular disease in Anhui Province
-
摘要:
目的 分析不同心血管疾病(cardiovascular disease, CVD)患病风险人群社区公共卫生综合干预血压控制效果。 方法 收集2016—2020年安徽省社区公共卫生综合干预资料(包括基线、3个月、12个月随访数据),采用《中国心血管疾病风险评估和管理指南》推荐的10年CVD风险评估模型将研究对象分为心血管疾病高危和非高危人群,比较高危和非高危人群社区公共卫生综合干预血压控制效果。 结果 共随访3 755名研究对象,CVD高危人群645人,标化检出率10.9%。随访12个月与基线相比,高危人群SBP和DBP分别下降了16.47 mm Hg(95% CI:-18.09~-14.86)、2.66 mm Hg(95% CI:-3.63~-1.69),非高危人群SBP和DBP分别下降了10.43 mm Hg(95% CI:-11.16~-9.70)、2.41 mm Hg(95% CI:-2.81~-2.01);3个月与基线相比,高危人群SBP和DBP分别下降了12.27 mm Hg(95% CI:-13.88~-10.65)、3.66 mm Hg(95% CI:-4.54~-2.77),非高危人群SBP和DBP分别下降了6.05 mm Hg(95% CI:-6.80~-5.30)、2.61 mm Hg(95% CI:-3.00~-2.23)。高危人群随访3个月后SBP下降水平、随访12个月后SBP和DBP下降水平明显高于非高危组(t=-5.100,t=-5.873,t=-2.729,均有P<0.05)。 结论 社区公共卫生综合干预对CVD高危人群血压改善优于非高危人群。因此,未来的公共卫生工作应进一步关注非高危人群。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the effect of comprehensive community public health intervention on blood pressure control among people with different cardiovascular disease (CVD) risks. Methods Comprehensive intervention data of community public health in Anhui Province were collected from 2016 to 2020 (including baseline, 3-month, and 12-month follow-up data). The 10-year cardiovascular disease risk assessment model recommended by China's CVD risk assessment and management guidelines was utilized to divide subjects into high-risk and low-risk CVD. The effects of the comprehensive community public health intervention on blood pressure control between the groups were compared. Results A total of 3 755 subjects were followed up, 645 patients with a high risk of CVD were detected, and the standardized detection rate was 10.9%. At the 12-month follow-up compared to baseline, SBP and DBP decreased by 16.47 mm Hg (95% CI: -18.09--14.86) and 2.66 mm Hg (95% CI: -3.63--1.69) for the high-risk group, and by 10.43 mm Hg (95% CI: -11.16--9.70) and 2.41 mm Hg (95% CI: -2.81--2.01) respectively for the low-risk group. In addition, at the 3-month follow-up compared to baseline, SBP and DBP decreased by 12.27 mm Hg (95% CI: -13.88--10.65) and 3.66 mm Hg (95% CI: -4.54--2.77) for high-risk CVD group, and by 6.05 mm Hg (95% CI: -6.80--5.30) and 2.61 mm Hg (95% CI: -3.00--2.23) respectively for the low-risk group. At the same time, the decrease in SBP for the high-risk CVD group after 3 months of follow-up and for both types of blood pressure after 12 months of follow-up were significantly more significant than those of the low-risk group (t=-5.100, t=-5.873, t=-2.729; all P < 0.05). Conclusions The comprehensive community public health intervention was effective at improving the blood pressure in both CVD risk groups but more effective for the high-risk group. Therefore, paying more attention to low-risk CVD populations is vital in designing future public health interventions. -
Key words:
- Cardiovascular disease /
- Hypertension /
- Influencing factors /
- Comprehensive intervention
-
表 1 10年CVD不同风险人群基线特征[n(%)]
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of different CVD risk groups in 10 years [n(%)]
组别 非高危人群(n=3 110) 高危人群(n=645) 合计(N=3 755) χ2值 P值 性别 359.896 <0.001 女 2 080(66.88) 172(26.67) 2 252(59.97) 男 1 030(33.12) 473(73.33) 1 503(40.03) 城乡 0.002 0.965 农村 1 946(62.57) 403(62.48) 2 349(62.56) 城市 1 164(37.47) 242(37.52) 1 406(37.44) 职业 68.494 <0.001 其他 1 331(42.80) 163(25.27) 1 494(39.79) 农民 1 779(57.20) 482(74.73) 2 261(60.21) 婚姻状况 0.530 0.467 未婚 373(11.99) 84(13.02) 457(12.17) 已婚 2 737(88.01) 561(86.98) 3 298(87.83) 地区 58.838 <0.001 南方 1 361(43.76) 177(27.44) 1 538(40.96) 北方 1 749(56.24) 468(72.56) 2 217(59.04) 饮酒情况 79.215 <0.001 否 2 608(83.86) 444(68.84) 3 052(81.28) 是 502(16.14) 201(31.16) 703(18.72) 吸烟情况 167.110 <0.001 否 2 629(84.53) 403(62.48) 3 032(80.75) 是 481(15.47) 242(37.52) 723(19.25) 年龄分组(岁) -14.339 a <0.001 35~ < 50 567(18.23) 27(4.19) 594(15.82) 50~ < 65 1 457(46.85) 205(31.78) 1 662(44.26) 65~75 1 086(34.92) 413(64.03) 1 499(39.92) BMI(kg/m2) -3.136 a 0.002 < 18.5 46(1.48) 13(2.02) 59(1.57) 18.5~ < 24.0 1 126(36.21) 266(41.24) 1 392(37.07) 24.0~ < 28.0 1 329(42.73) 270(41.86) 1 599(42.58) ≥28.0 609(19.58) 96(14.88) 705(18.77) 文化程度 -5.137 a <0.001 小学及以下 2 128(68.42) 504(78.14) 2 632(70.09) 初中 649(20.87) 104(16.12) 753(20.05) 高中 217(6.98) 29(4.50) 246(6.55) 大学及以上 116(3.73) 8(1.24) 124(3.30) 家庭年收入(元) -3.250 a 0.001 < 10 000 686(22.06) 179(27.75) 865(23.04) 10 000~ < 50 000 1 907(61.32) 378(58.60) 2 285(60.85) >50 000 517(16.62) 88(13.64) 605(16.11) 注:a使用Mann-Whitney U检验。 表 2 10年CVD不同风险人群血压各阶段差值的均数及95% CI
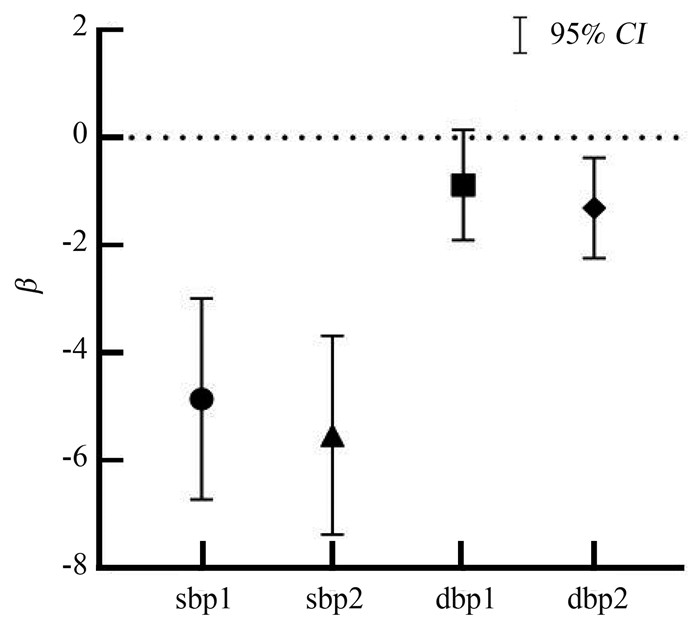
Table 2. Mean values and 95% CI of blood pressure differences at different stages in populations at different risk of CVD in 10 years
变量 高危人群(n=645) 非高危人群(n=3 110) x值 95% CI x值 95% CI sbp1 -16.47 -18.09~-14.86 -10.43 -11.16~-9.70 sbp2 -12.27 -13.88~-10.65 -6.05 -6.80~-5.30 dbp1 -2.66 -3.63~-1.69 -2.41 -2.81~-2.01 dbp2 -3.66 -4.54~-2.77 -2.61 -3.00~-2.23 注:sbp1:基线后12个月SBP-基线SBP;sbp2:基线后3个月SBP-基线SBP;dbp1:基线后12个月DBP-基线DBP;dbp2:基线后3个月DBP-基线DBP。 表 3 血压控制效果影响因素的单因素分析结果[M(P25,P75)]
Table 3. Results of univariate analysis of influencing factors of blood pressure control effect [M(P25, P75)]
组别 sbp1 Z/H值 P值 sbp2 Z/H值 P值 dbp1 Z/H值 P值 dbp2 Z/H值 P值 性别 -1.883 0.060 -0.435 0.664 -3.019 0.003 -1.534 0.125 女 -11.0
(-12.0, -9.5)-5.5
(-6.5, -4.5)-2.0
(-2.5, -1.0)-2.0
(-2.0, -1.0)男 -9.5
(-10.5, -7.5)-6.0
(-7.5, -4.0)-3.0
(-3.5, -2.0)-2.5
(-3.0, -1.5)城乡 -1.927 0.054 -5.042 < 0.001 -7.105 < 0.001 -9.892 < 0.001 农村 -11.0
(-12.0, -9.5)-4.5
(-5.5, -3.0)-3.0
(-3.0, -2.5)-1.0
(-1.0, -0.5)城市 -9.5
(-10.5, -7.5)-8.5
(-9.5, -7.0)-0.5
(-1.0, 1.0)-4.5
(-5.0, -3.5)职业 -3.762 < 0.001 -1.744 0.081 -6.326 < 0.001 -4.134 < 0.001 其他 -8.0
(-9.5, -6.5)-4.5
(-5.5, -3.0)-3.5
(-4.0, -2.5)-3.0
(-3.5, -2.0)农民 -12.0
(-13.0, -10.5)-6.5
(-7.5, -5.0)-1.5
(-2.0, -0.5)-2.0
(-2.5, -1.5)婚姻状况 -0.484 0.629 -1.848 0.065 -2.369 0.018 -1.060 0.289 未婚 -11.0
(-14.0, -8.5)-7.5
(-10.0, -4.5)-1.5
(-2.5, -0.5)-2.0
(-3.0, -0.5)已婚 -10.5
(-11.0, -9.0)-5.5
(-6.0, -4.5)-2.5
(-2.5, -2.0)-2.5
(-2.5, -2.0)地区 -5.608 < 0.001 -1.805 0.071 -7.299 < 0.001 -3.797 < 0.001 南方 -8.0
(-9.0, -6.5)-5.0
(-6.5, -3.5)-3.5
(-4.0, -2.5)-3.0
(-3.5, -2.0)北方 -12.5
(-13.5, -11.0)-6.0
(-7.0, -5.0)-1.5
(-1.5, -0.5)-2.0
(-2.5, -1.5)饮酒情况 否 -10.0
(-10.5, -8.5)-0.499 0.618 -5.5
(-6.5, -4.5)-0.530 0.596 -2.0
(-2.0,-1.5)-3.375 0.001 -2.5
(-2.5, -2.0)-1.501 0.133 是 -11.5
(-13.0, -9.0)-7.5
(-9.0, -5.0)-3.5
(-4.0,-2.5)-2.5
(-3.0, -1.5)吸烟情况 -2.198 0.028 -1.553 0.120 -0.828 0.408 -0.378 0.705 否 -10.5
(-11.0, -9.0)-6.0
(-6.5, -5.0)-2.0
(-2.0,-1.0)-2.5
(-2.5, -2.0)是 -9.5
(-11.0, -7.0)-5.0
(-6.5, -3.5)-2.5
(-3.0, -1.5)-2.0
(-3.0, -1.0)年龄分组(岁) 62.356 < 0.001 38.666 < 0.001 9.234 0.010 4.183 0.124 35~ < 50 -4.8
(-6.5, -3.0)-1.5
(-3.0, 0.0)-2.5
(-3.0, -1.0)-1.0
(-1.5, 0.0)50~ < 65 -9.5
(-10.5, -8.0)-4.5
(-5.5, -3.5)-2.5
(-3.0, -1.5)-3.0
(-3.5, -2.0)65~75 -14.0
(-15.0, -12.5)-9.0
(-10.5, -7.5)-2.0
(-2.5, -1.0)-2.0
(-2.0, -1.0)BMI(kg/m2) 3.991 0.262 1.977 0.577 0.464 0.927 11.185 0.011 < 18.5 -13.0
(-20.5, -4.0)-4.0
(-11.0, 0.5)-2.0
(-6.5, 2.0)0.0
(-1.0, 4.0)18.5~ < 24.0 -9.0
(-10.5, -7.5)-5.5
(-6.5, -4.0)-2.3
(-3.0, -1.5)-2.0
(-2.5, -1.0)24.0~ < 28.0 -10.5
(-12.0, -8.5)-5.5
(-6.5, -4.5)-2.5
(-3.0, -1.5)-3.0
(-3.5, -2.0)≥28.0 -12.0
(-13.5, -10.0)-7.0
(-8.5, -5.0)-2.5
(-3.0, -1.5)-3.0
(-3.5, -1.5)文化程度 23.930 < 0.001 16.532 0.001 25.949 < 0.001 1.452 0.693 小学及以下 -12.0
(-13.0, -10.5)-6.5
(-7.0, -5.0)-2.0
(-2.5, -1.0)-2.5
(-3.0, -2.0)初中 -8.0
(-9.5, -6.5)-3.5
(-5.0, -1.5)-4.0
(-4.5, -2.5)-2.0
(-2.5, -1.0)高中 -6.0
(-7.0, -3.5)-3.5
(-6.0, -1.0)-2.0
(-3.0, 0.0)-2.0
(-3.5, -0.5)大学及以上 -7.5
(-11.0, -2.5)-7.0
(-9.0, -2.5)-4.0
(-6.0, -2.5)-3.0
(-4.5, -0.5)家庭年收入(元) 23.101 < 0.001 0.478 0.787 30.393 < 0.001 8.561 0.014 <10 000 -14.0
(-15.5, -11.5)-6.0
(-7.5, -4.5)-2.0
(-2.5, -1.0)-1.5
(-2.0, -0.5)10 000~ < 50 000 -9.5
(-10.5, -8.0)-6.0
(-7.0, -4.5)-1.5
(-2.0, -0.5)-3.0
(-3.5, -2.0)>50 000 -9.5
(-11.0, -6.5)-5.0
(-6.5, -3.0)-4.5
(-5.5, -3.5)-2.0
(-2.5, -1.0)注:sbp1:基线后12个月SBP-基线SBP;sbp2:基线后3个月SBP-基线SBP;dbp1:基线后12个月DBP-基线DBP;dbp2:基线后3个月DBP-基线DBP。 表 4 血压控制效果影响因素的多因素分析结果
Table 4. Results of multivariate analysis of influencing factors of blood pressure control effect
因变量 自变量 偏回归系数 标准误差 偏回归系数(标准化) t值 P值 sbp1 常量 -0.334 2.889 -0.116 0.908 地区 -4.075 0.736 -0.096 -5.538 <0.001 吸烟 1.712 0.867 0.032 1.976 0.048 年龄(岁) -3.324 0.519 -0.112 -6.411 <0.001 sbp2 常量 2.246 1.804 1.245 0.213 城乡 -3.506 0.720 -0.079 -4.871 <0.001 年龄(岁) -2.179 0.522 -0.072 -4.176 <0.001 dbp1 常量 -14.813 2.413 -6.140 <0.001 城乡 4.111 0.398 0.172 10.339 <0.001 职业 2.193 0.451 0.093 4.860 <0.001 地区 3.035 0.403 0.129 7.535 <0.001 性别 0.904 0.439 0.038 2.060 0.039 家庭年收入(元) -0.927 0.334 -0.050 -2.774 0.006 dbp2 常量 1.627 1.356 1.200 0.230 城乡 -3.142 0.382 -0.137 -8.218 <0.001 地区 0.846 0.390 0.038 2.168 0.030 BMI(kg/m2) -0.637 0.239 -0.044 -2.671 0.008 注:sbp1:基线后12个月SBP-基线SBP;sbp2:基线后3个月SBP-基线SBP;dbp1:基线后12个月DBP-基线DBP;dbp2:基线后3个月DBP-基线DBP。 -
[1] Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American heart association[J]. Circulation, 2019, 139(10): e56-e528. DOI: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659. [2] 胡盛寿, 高润霖, 刘力生, 等. 《中国心血管病报告2018》概要[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2019, 34(3): 209-220. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2019.03.001.Hu SS, Gao RL, Liu LS, et al. Summary of the 2018 report on cardiovascular diseases in China[J]. Chin Circul J, 2019, 34(3): 209-220. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2019.03.001. [3] 中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组. 中国心血管健康与疾病报告2020概要[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2021, 36(6): 521-545. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2021.06.001.The writing committee of the report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China. annual report on cardiovascular health and diseases in China 2020[J]. Chin Circul J, 2021, 36(6): 521-545. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2021.06.001. [4] 中国心血管病风险评估和管理指南编写联合委员会. 中国心血管病风险评估和管理指南[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2019, (1): 13-35. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2019.01.004.The joint task force for guideline on the assessment and management of cardiovascular risk in China. guideline on the assessment and management of cardiovascular risk in China[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2019, (1): 13-35. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2019.01.004. [5] Han C, Liu FC, Yang XL, et al. Ideal cardiovascular health and incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease among Chinese adults: the China-PAR project[J]. Sci China Life Sci, 2018, 61(5): 504-514. DOI: 10.1007/s11427-018-9281-6. [6] 刘红. 社区公共卫生护理在心血管疾病防治中的应用[J]. 中国卫生标准管理, 2021, 12(8): 151-153. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9316.2021.08.055.Liu H. Application of community public health nursing in prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease[J]. China Health Stand Mana, 2021, 12(8): 151-153. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9316.2021.08.055. [7] 郭丽花, 钟节鸣, 方乐, 等. 心血管疾病高危人群临床预防性服务和生活方式调整综合干预效果评价[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2020, 54(4): 411-415. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20190606-00453.Guo LH, Zhong JM, Fang L, et al. Evaluation on the effect of comprehensive intervention combined with clinical preventive services and lifestyle adjustment among high-risk populations of cardiovascular disease in Tongxiang City[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2020, 54(4): 411-415. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20190606-00453. [8] Torralbas-Ortega J, Paños-Martínez M, Patró-Moncunill E, et al. Efficacy of a short psychoeducational group intervention for the prevention of cardiovascular risk in patients with severe mental disorder: a randomized trial[J]. J Nerv Ment Dis, 2020, 208(3): 222-229. DOI: 10.1097/NMD.0000000000001081. [9] O'Connor LE, Li J, Sayer RD, et al. Short-Term effects of healthy eating pattern cycling on cardiovascular disease risk factors: pooled results from two randomized controlled trials[J]. Nutrients, 2018, 10(11): 1725. DOI: 10.3390/nu10111725. [10] Yang X, Li J, Hu D, et al. Predicting the 10-Year risks of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in Chinese population: the China-par project (prediction for ASCVD risk in China)[J]. Circulation, 2016, 134(19): 1430-1440. DOI: 10.1161/circulationaha.116.022367. [11] 吴超群, 李希, 路甲鹏, 等. 中国居民心血管疾病危险因素分布报告[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2021, 36(1): 4-13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2021.01.002.Wu CQ, Li X, Lu JP, et al. Report on geographical disparity of cardiovascular risk factors in China[J]. Chin Circul J, 2021, 36(1): 4-13. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2021.01.002. [12] 李方启, 张伟, 朱广余. 安徽人口老龄化与养老产业问题探析[J]. 统计科学与实践, 2021, (10): 25-28. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8905.2021.10.007.Li FQ, Zhang W, Zhu GY. On the aging population and pension industry in Anhui Province[J]. Statistical Theory and Practice, 2021, (10): 25-28. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8905.2021.10.007. [13] 胡光辉, 陈桂梅, 杨冉, 等. 安徽农村居民饮食习惯调查分析[J]. 皖南医学院学报, 2011, 30(5): 419-421. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0217.2011.05.026.Hu GH, Chen GM, Yang R, et al. A survey on diet habits of rural residents in Anhui province[J]. Acta Acad Med Wanna, 2011, 30(5): 419-421. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0217.2011.05.026. [14] 舒强, 熊华利, 邱建平, 等. 重庆市荣昌区35~75岁居民高血压患病率、知晓率、治疗率、控制率及相关影响因素[J]. 实用预防医学, 2022, 29(6): 652-657. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2021.12.004.Shu Q, Xiong HL, Qiu JP, et al. Current status of key indicators about diabetes prevention, control and management and its influencing factors among residents aged 35-75 years in Chongqing Municipality[J]. Pract Prev Med, 2022, 29(6): 652-657. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2021.12.004. [15] 赵廷明, 李鑫, 向静, 等. 四川省通江县35~75岁高血压患者的高血压知晓率、治疗率、控制率及其影响因素分析[J]. 疾病预防控制通报, 2022, 37(4): 1-7. DOI: 10.13215/j.cnki.jbyfkztb.2205002.Zhao TM, Li X, Xiang J, et al. Analysis of rate of awareness, treatment and control of hypertension and influencing factors in hypertensives aged 35-75 years in Tongjiang county, Sichuan province[J]. Endemic Diseases Bulletin, 2022, 37(4): 1-7. DOI: 10.13215/j.cnki.jbyfkztb.2205002. [16] Soltani S, Saraf-Bank S, Basirat R, et al. Community-based cardiovascular disease prevention programmes and cardiovascular risk factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Public Health, 2021, 200: 59-70. DOI: 10.1016/j.puhe.2021.09.006. [17] Álvarez-Bueno C, Cavero-Redondo I, Martínez-Andrés M, et al. Effectiveness of multifactorial interventions in primary health care settings for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review of systematic reviews[J]. Prev Med, 2015, 76, Suppl: S68-S75. DOI: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2014.11.028. -





 下载:
下载: